1. Objective
Implement network segmentation between workloads across multi-cloud and on-premises environments using network domains.
Green VPC resources in AWS and Azure can communicate with each other, while access is restricted to Blue VPC resources in GCP. Later, we will ease this restriction with a connection policy; Blue and Green segments will be able to communicate with others as well.
NOTE: Network Segmentation will be extended to on-premises in the Site2Cloud lab.
2. Network Segmentation Overview
Enterprises can define their network domains (aka segments) and group VNets/VPCs/VCNs with similar security policies without requiring firewall solutions.
Aviatrix transit and spokes architecture help enterprises create customised segments and onboard branches, partners and customers in their respective segments so no partner can communicate with each other unless desired.
3. Topology
In this lab, we will use Aviatrix CoPilot to enable Network Segmentation in Azure, AWS and GCP, in order to segregate VPC/VNet with similarities. At this point, there is a flat routing domain and the communication among the three CSPs occurs through the Transit Core Backbone layer.
4. Configuration
Note: Network Segmentation can be configured from the Controller and CoPilot.
In this lab, we will configure it from CoPilot.
4.1. Aviatrix Transit Gateways
Go to CoPilot > Networking > Network Segmentation > Network Domains > Transit Gateways:
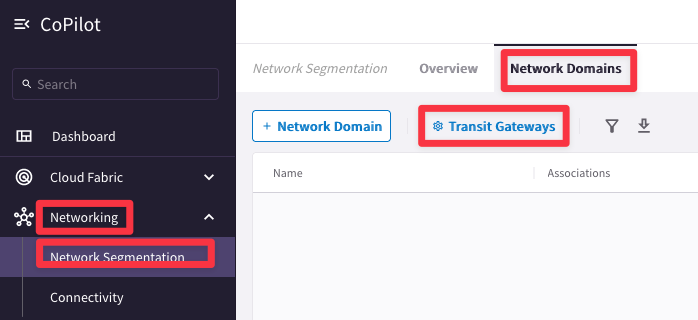
Enable all three Aviatrix Transit Gateways in Azure, GCP and AWS (us-east-2 only for now) for network segmentation as shown below:

4.2 Network Domains
Go to CoPilot > Networking > Network Segmentation > Network Domains > + Network Domain
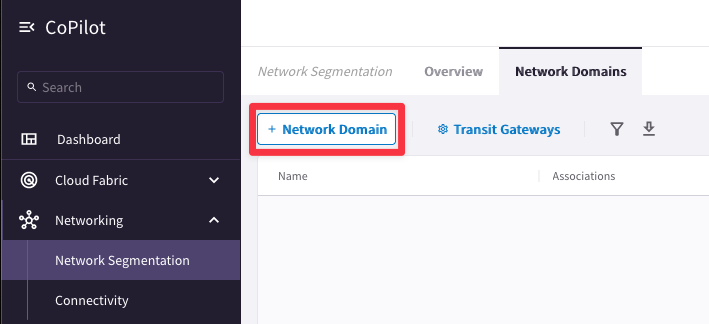
Create two network domains (Green and Blue) and associate them to their respective Spokes as follows:
- Green - azure-us-west-spoke1 (do not select azure-us-west-spoke2)
- Green - aws-us-east2-spoke1 (do not select aws-us-east1-spoke1)
- Blue - gcp-us-central1-spoke1
Click Save after creating each Network Domain


5. Verification of Segment Attachment
This is what the lab topology looks like after enabling network segmentation:
5.1. CoPilot Verification
Go to CoPilot > Networking > Network Segmentation > Network Domains.
Verify the segments and the associations as shown below:

Go to CoPilot > Cloud Fabric > Gateways > Transit Gateways and select the Transit Gateway aws-us-east2-transit:
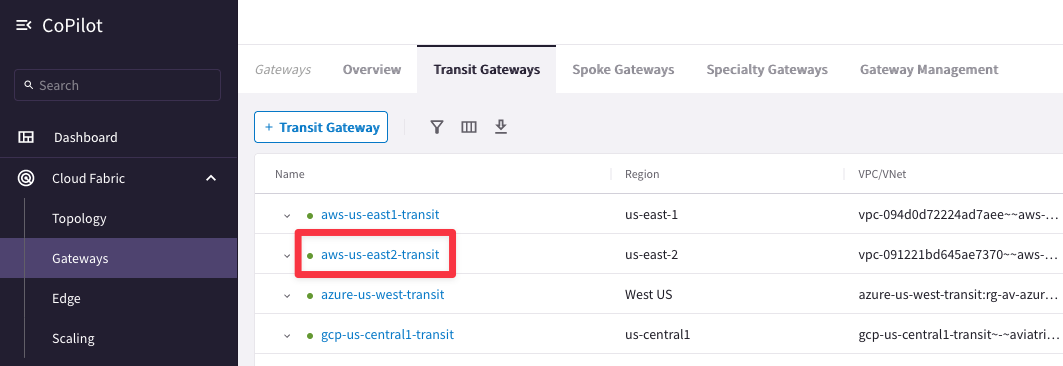
Then select the "Gateway Routes" tab and inspect the routing table of the network domain Green, likewise the routing table of the network domain Blue:


Go to CoPilot > Networking > Network Segmentation > Overview > Logical View
Nodes represent spokes and site2cloud instances. Hover over a node to highlight reachability. Nodes are grouped by colored arcs representing network domains. At this time, only the spoke gateways in Azure and AWS (i.e. Green Network Domain) are connected:

Open three terminal windows and SSH to the test instances/VMs in each cloud and ping the private IPs of each other to test the Multicloud connectivity (Refer to pod info).
Azure and AWS resources will ping each other, but neither will be able to access GCP VM, since GCP spoke is in a different segment (Blue).
AWS:
SSH into aws-us-east2-spoke1-test1 (ssh student@public_ip)

Azure:
SSH into azure-us-west-spoke1-test1 (ssh student@public_ip)

GCP:
SSH into gcp-us-central1-spoke1-test1 (ssh student@public_ip)

6. Connection Policy
Go to CoPilot > Networking > Network Segmentation > Network Domains
Click the pencil icon to edit. You can either select the Green domain or the Blue domain: the connection policy is always bidirectional!

Select the appropriate option from the Connect to Network Domain pull-down menu (Green shown here). Then click Save:

6.1. Verification of Connection Policy
Go to CoPilot > Networking > Network Segmentation > Overview > Logical View
Now you will see that the spoke gateways in all three clouds are connected. This is because the Blue and Green Network Domains are directly connected:

Retest the connectivity; now you will have end-to-end connectivity across a multicloud environment.
AWS:
SSH into aws-us-east2-spoke1-test1 (ssh student@public_ip)

Azure:
SSH into azure-us-west-spoke1-test1 (ssh student@public_ip)

GCP:
SSH into gcp-us-central1-spoke1-test1 (ssh student@public_ip)

After this lab, this is how the overall topology would look like:
