AWS: Quick Review
There is no doubt, we are now in the cloud networking age. For roughly the last decade system engineers and IT architects have searched for a way to deploy sophisticated infrastructure and applications in the cloud.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is one of the cloud providers able to facilitate the necessary infrastructure, constructs, and services IT professionals require. Infrastructure refers to physical data centers and networking. This portion is managed by AWS. Constructs/Services typically fall under one of these three categories: network, storage, or compute. It is up to the consumer of AWS to deploy, connect, and manage these services.
So, now that we have some context regarding AWS, here is the flow. We are going to learn:
· What is the AWS console?
· Getting started with the console
· Exploring console features
· The future of the AWS Console
What is the AWS Console?
In short, the AWS Console is a web-based user portal which, provides access to native cloud constructs and services. The console offers users an inbuilt interface to perform tasks such as provisioning resources, user, and billing management.
Getting started with the AWS Console
To get started you will need to have an AWS account, and a web browser installed on your computer. To access the AWS console, you will need to perform the following:
1. Open a web browser
2. Enter the URL http://aws.amazon.com/console/ to access the AWS management console.
3. Click the create new account button in the top right of the page
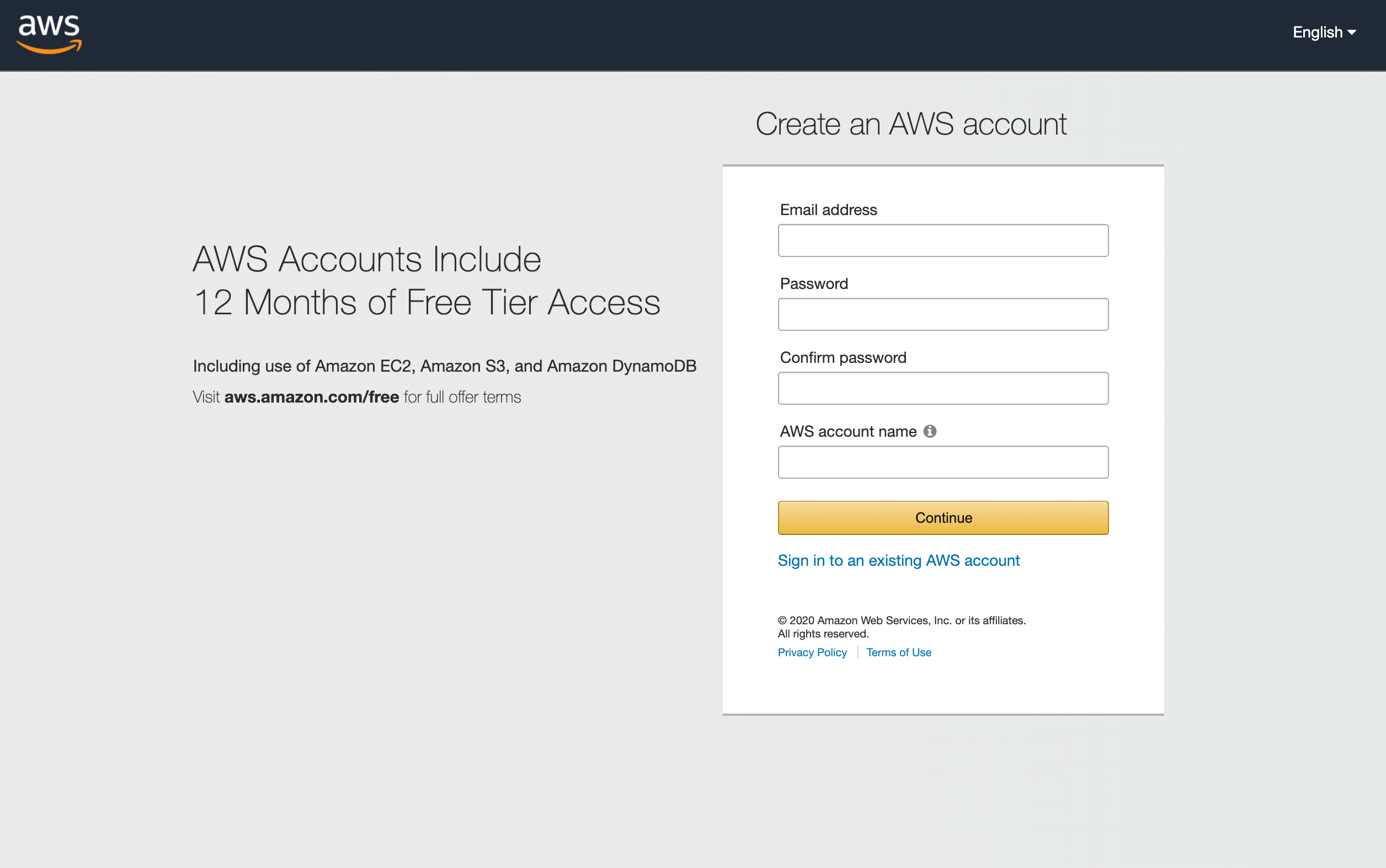
4. Fill in the fields below and hit continue
Note: Apart from accessing the AWS console through a web browser, you can also access it through the mobile app version. If you’re using a mobile phone, click here to get started on the mobile app.
Exploring Console Features
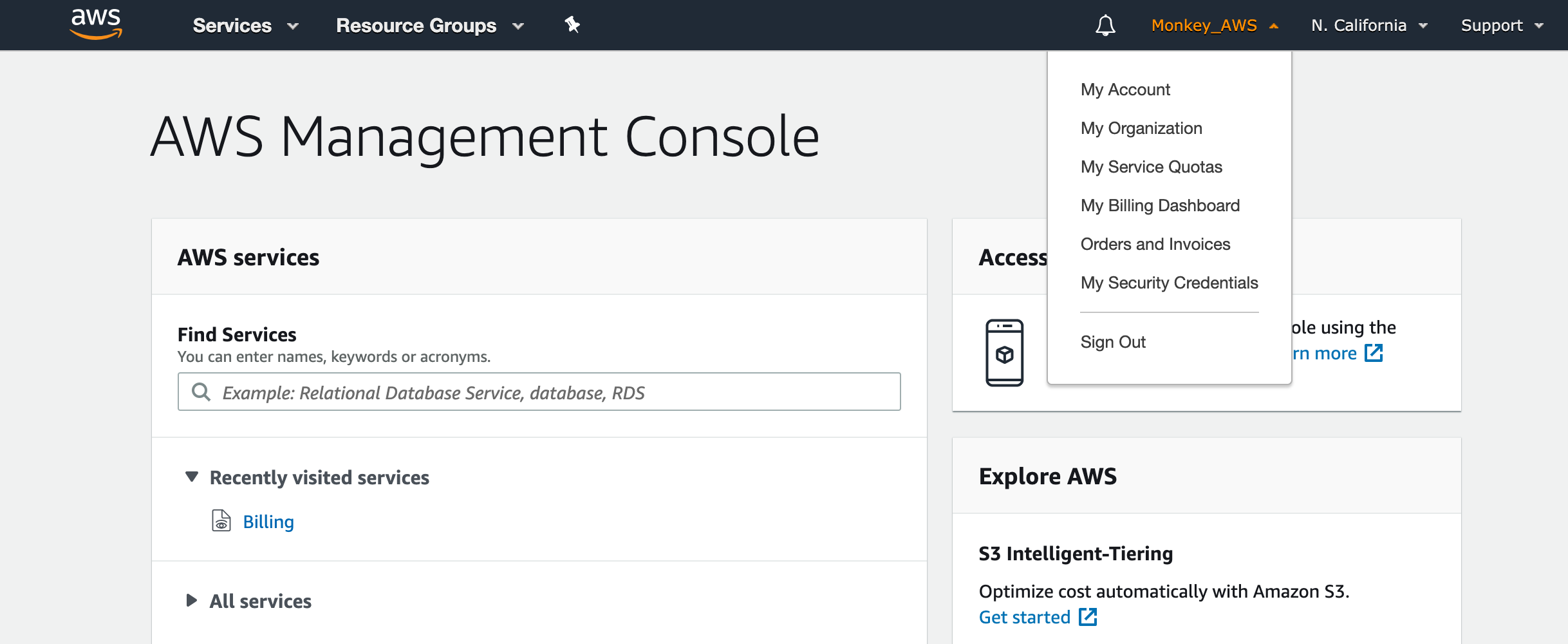
Once you have logged-in you will see the landing page like the one shown below. As stated above, you can access the console from essentially anywhere with access to the internet.
Navigation Tips:
· The AWS banner at the top will remain in that configuration during the use of the console
· Click the AWS logo at any time to return to the main landing page
· Open different areas of the console by right clicking and opening a new tab. This allows much faster navigation.
On the far-right side of the banner is the support button. Here you can log support tickets (with the proper support plan). Next, to that you can choose the geographic region where you wish to deploy your cloud resources and services. At this present time, AWS offers 22 regions. However, not all regions support every AWS service or feature.
AWS offers a variety of services which you can access and manage from this one account. Currently there are 217 services, with some being added and removed all the time. The image below shows an expanded list of some the services available.
Almost all services must be deployed in a specific region. For example, having multiple Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) resources in different areas across the globe. This is because these VPCs can be thought of as distinct data centers in the cloud. Contrast this to the services S3 or IAM which are global services. When these are selected you will see the region on the banner change to “Global” and you cannot pick a region.
Tips:
· Click the thumb tack icon on the top banner to pin your favorite services to the banner for quick access.
Using the search bar, it might make it easier to find the services you need. One of the areas to search for is the AWS Marketplace. Here you find third-party software and services. Companies such as Microsoft, Splunk, Palo Alto Networks, and Aviatrix have products listed on the marketplace.
The future of the AWS Console
A web-based console format fits the consumption of AWS well. The first AWS console was launched way back in the 1990s. Comparing it to the present iteration, we would all say it is slow and ugly: built with a Netscape interface.
Overall the console will likely remain fairly similar for the foreseeable future. AWS is much more focused on infrastructure and service improvements. In the few years I have been playing with AWS little in the UI has changed. However, keeping up with feature changes is a full-time job.
