Introduction
Aviatrix Controller needs to be able to resolve DNS queries, communicate with Aviatrix gateways, download software, redirect inbound SAML VPN connection etc and hence it is strongly recommended that the instance size of controller follow measures suggested by Aviatrix Controller startup guide.
Since it is the critical component of Aviatrix platform, in this blog we will discuss different methodologies of deploying Controller HA in AWS for seamless experience when failure happens.
At present, Aviatrix supports automatic Controller failover when HA is deployed in same AWS region (can be different AZ)
Case 1 - Controller HA in same AWS region
Aviatrix Controller HA rely on AWS auto scaling group with capacity of 1. If Controller EC2 is stopped or terminated by any reason, it will be re-deployed by the Auto scaling group. This use case works with AWS Lambda script which launches HA controller using Auto scaling group. We will need access to S3 bucket from both the controllers with appropriate permissions.
- Details on how to enable controller HA in same AWS region can be found here Controller HA in AWS.
- In case of controller HA event failure (incorrect permissions, cloud formation stack lambda pointing to the wrong backup path etc) we can manually restore the backup on the new controller (as explained in Case 2 below).
Case 2 - Controller HA in different AWS region
At present, we do not support Controller HA in two different AWS regions and detect one or the other failure automatically. Our current Controller HA script leverages EC2 auto scaling. EC2 auto scaling does not support cross region but it does support cross AZs.
Some customers may need HA controllers in two different regions for DR. This is rather a manual procedure as discussed below (can easily be automated as per customer environment).
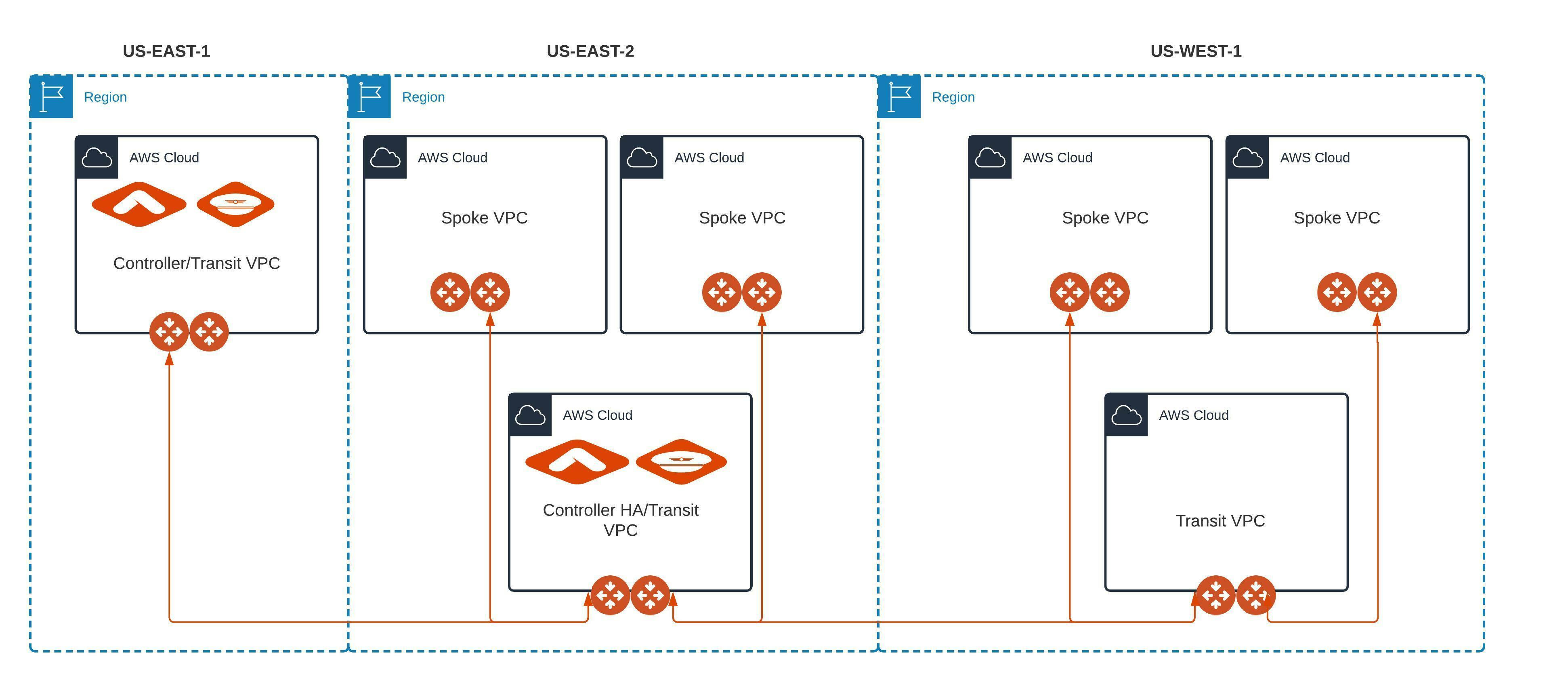
Let's understand this with the help of an example. As shown in topology diagram, we deployed Aviatrix Controller in US-EAST-1, with its transit gateways connected to transit gateways in US-EAST-2 and US-WEST-1 (full mesh). Transit gateways are also connected to spoke gateways as shown.
To demonstrate cross region manual Controller HA, we deployed Controller HA in US-EAST-2 region as well.
For visibility, operational view, health monitor etc we also deployed Aviatrix CoPilot from AWS marketplace.
Now, we have 2 controllers one in US-EAST-1 (active) and another in US-EAST-2 (non-active/stopped) and following are the steps to demonstrate manual failover.
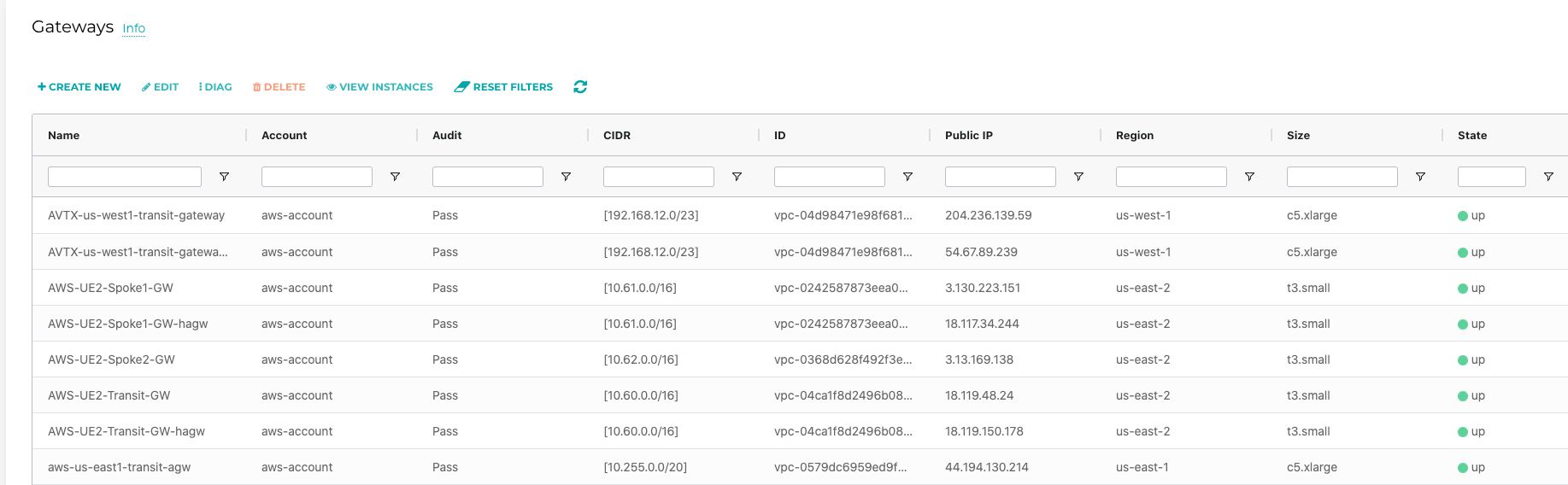
- Gateway states from active controller are shown as below before Controller HA test
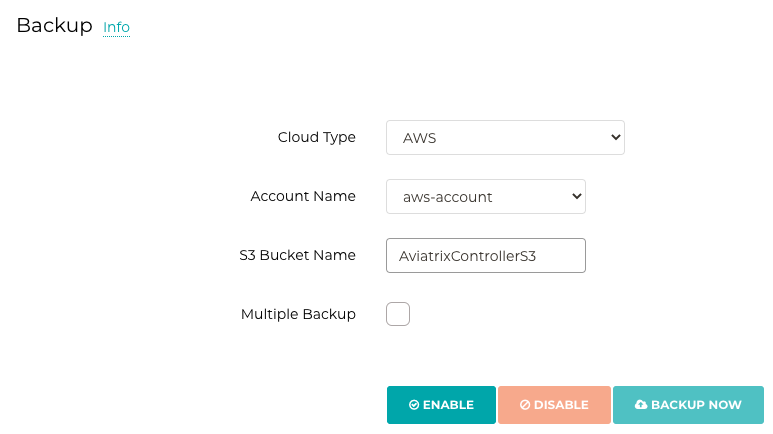
- On active controller, Go to Settings -> Maintenance -> Back up and restore -> Restore configuration to S3 bucket (need AWS access account key or add the access account in controller)
- Allocate Elastic IP to new controller
- Add required IAM roles
- Onboard CSP accounts on the new controller so it can access S3 or similar buckets in other CSPs.
- We have backed up our configuration from controller in US-EAST-1 in S3 bucket (every night at 12 AM configurations will be automatically backed up to S3)
- Now let’s assume AZ in US-EAST-1, where controller is deployed, is down from AWS end and we need to operate our applications from controller in US-EAST-2.
- To test, stop controller in US-EAST-1.
- Start controller in US-EAST-2 and under Settings -> Maintenance -> Restore -> provide S3 path and file name
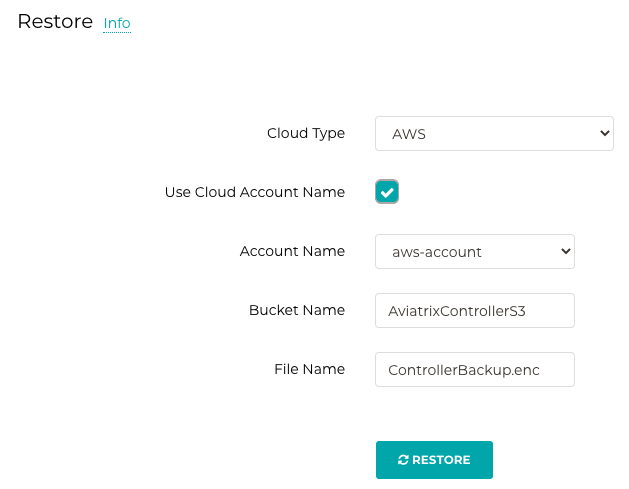
- Once restored, all gateways are UP in new-controller
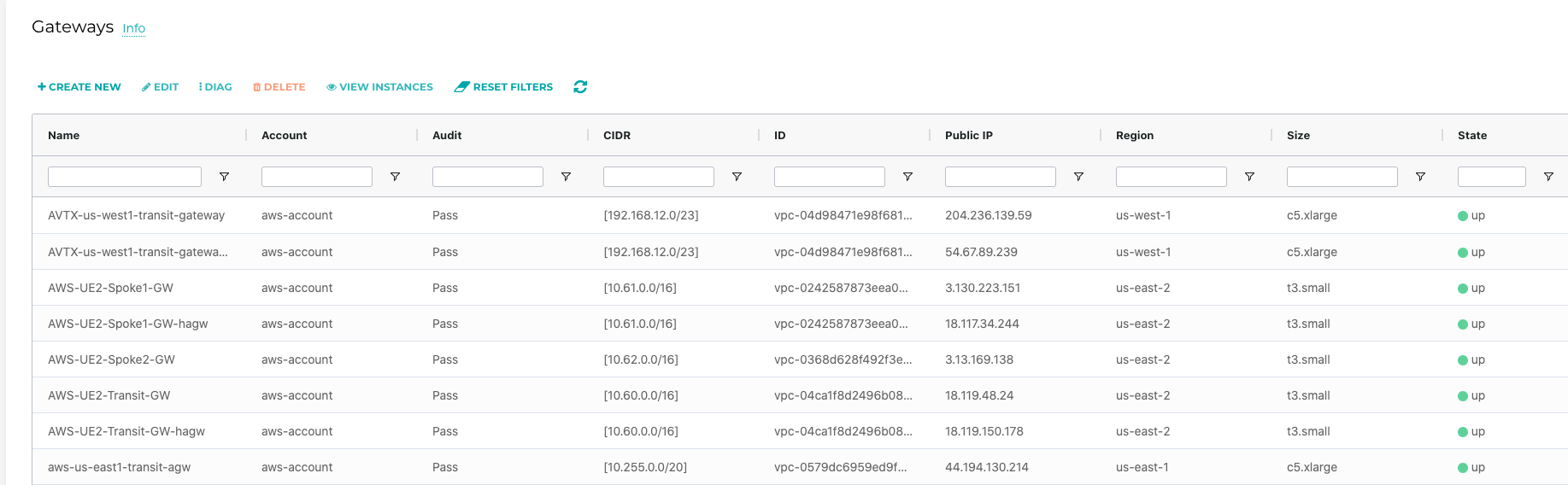
Observations
- In case of AZ failures, customers should keep Aviatrix Controllers in a separate AZ than other Aviatrix gateways (transit, spoke and stand-alone). That means EC2 placement for Controller and gateways should be crafted in different AZs.
- Even if elastic IP changes in new controller, unless we are using SAML authentications, configuration restore will work.
- Controller AMI version should be latest or at least in 6.0 series.
- We should back up our configurations to S3 regularly than default 24 hours, since in case of failure any new changes made within last 24 hours will be lost. (Depends on customer use cases and business needs)

