While creating an AWS Transit Gateway (TGW) attachment (either a VPC or a VPN attachment), AWS asks you to select at most one subnet per Availability Zone; however, it does not mean that you can only route traffic to resources in that one attached subnet.
The purpose of attaching one subnet per Availability Zone is to enable that Availability Zone to be used by the AWS Transit Gateway (TGW) to route traffic to ALL resources in VPC subnets. Once you specify one subnet in an Availability Zone, that Availability Zone gets enabled, and now AWS Transit Gateway (TGW) can route traffic to all the subnets in that Availability Zone - not just the single subnet it was initially attached to. Take a look at the following AWS article on this topic: AWS Article
However, the way AWS implements this currently can be confusing as they leave it to you to scan all the Availability Zones, then choose the subnet to connect to in each Availability Zone, and connect it to the VPC or VPN attachment. The console explicitly says, “you can only select one subnet per Availability Zone” but this is misleading – the attachment, while made to one subnet, is still enabling full connectivity to all the other subnets in the VPC. 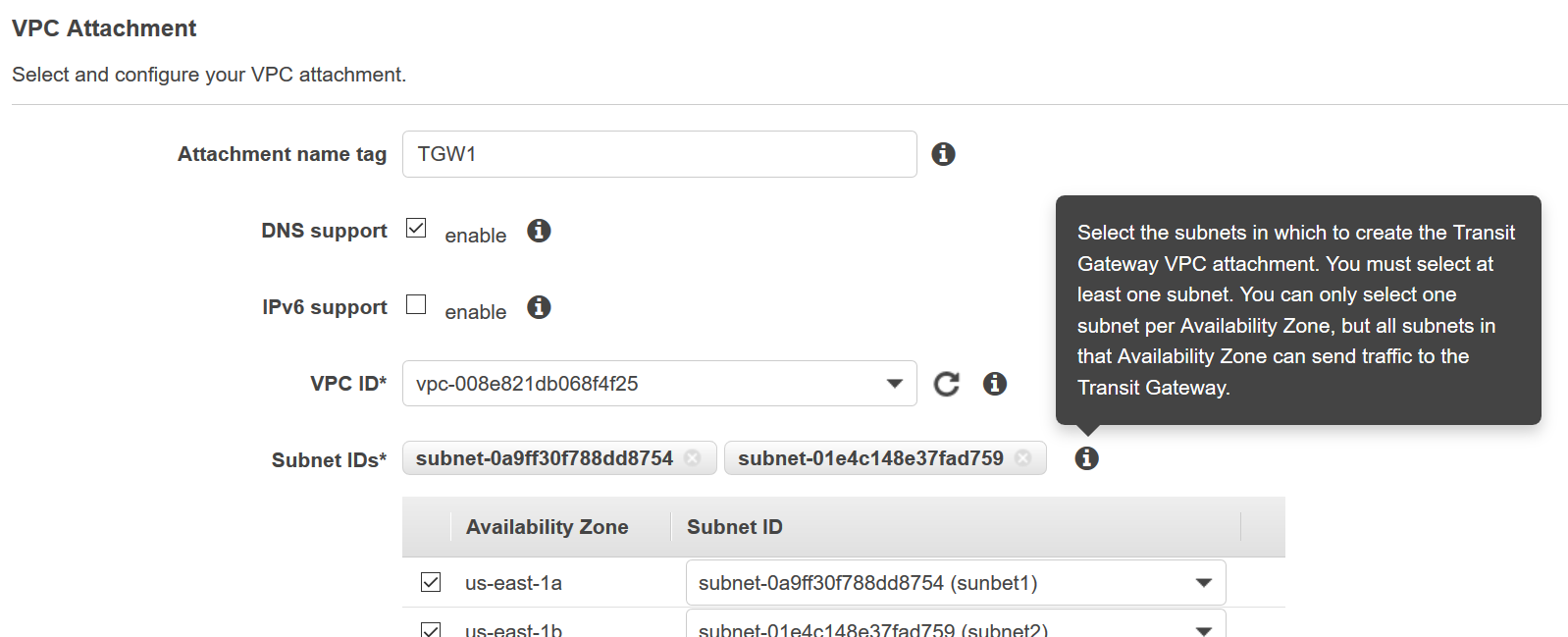
Aviatrix Multi-Cloud Networking platform makes this process much simpler. While building AWS Transit Gateway (TGW) using the Aviatrix Orchestrator feature, Aviatrix automatically scans all the Availability Zones in your VPC, choose one subnet per availability zone and connect it to the right attachment to ensure connectivity across subnets through the transit gateway. You can learn more about how the Aviatrix Orchestrator feature (available in the AVX Controller) extends and simplifies the AWS Transit Gateway (TGW) here.
